在英特尔 CPU 上微调 Stable Diffusion 模型
中文翻译: MatrixYao 校对: zhongdongy
本文也提供英文版本 English。
扩散模型能够根据文本提示生成逼真的图像,这种能力促进了生成式人工智能的普及。人们已经开始把这些模型用在包括数据合成及内容创建在内的多个应用领域。 Hugging Face Hub 包含超过 5 千个预训练的文生图 模型。这些模型与 Diffusers 库 结合使用,使得构建图像生成工作流或者对不同的图像生成工作流进行实验变得无比简单。
和 transformer 模型一样,你可以微调扩散模型以让它们生成更符合特定业务需求的内容。起初,大家只能用 GPU 进行微调,但情况正在发生变化!几个月前,英特尔 推出 了代号为 Sapphire Rapids 的第四代至强 CPU。Sapphire Rapids 中包含了英特尔先进矩阵扩展 (Advanced Matrix eXtension,AMX),它是一种用于深度学习工作负载的新型硬件加速器。在之前的几篇博文中,我们已经展示了 AMX 的优势: 微调 NLP transformers 模型、对 NLP transformers 模型进行推理,以及 对 Stable Diffusion 模型进行推理。
本文将展示如何在英特尔第四代至强 CPU 集群上微调 Stable Diffusion 模型。我们用于微调的是 文本逆向 (Textual Inversion) 技术,该技术仅需少量训练样本即可对模型进行有效微调。在本文中,我们仅用 5 个样本就行了!
我们开始吧。
配置集群
英特尔 的小伙伴给我们提供了 4 台托管在 英特尔开发者云 (Intel Developer Cloud,IDC) 上的服务器。IDC 作为一个云服务平台,提供了一个英特尔深度优化的、集成了最新英特尔处理器及 最优性能软件栈 的部署环境,用户可以很容易地在此环境上开发、运行其工作负载。
我们得到的每台服务器均配备两颗英特尔第四代至强 CPU,每颗 CPU 有 56 个物理核和 112 个线程。以下是其 lscpu 的输出:
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Address sizes: 52 bits physical, 57 bits virtual
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 224
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-223
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
Model name: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8480+
CPU family: 6
Model: 143
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 56
Socket(s): 2
Stepping: 8
CPU max MHz: 3800.0000
CPU min MHz: 800.0000
BogoMIPS: 4000.00
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc art arch_per fmon pebs bts rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc cpuid aperfmperf tsc_known_freq pni pclmulqdq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx smx est tm2 ssse3 sdbg fma cx16 xtpr pdcm pcid dca sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch cpuid_fault epb cat_l3 cat_l2 cdp_l3 invpcid_single intel_ppin cdp_l2 ssbd mba ibrs ibpb stibp ibrs_enhanced tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid ept_ad fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid cqm rdt_a avx512f avx512dq rdseed adx smap avx512ifma clflushopt clwb intel_pt avx512cd sha_ni avx512bw avx512vl xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1 xsaves cqm_llc cqm_occup_llc cqm_mbm_total cqm_mbm_local split_lock_detect avx_vnni avx512_bf16 wbnoinvd dtherm ida arat pln pts hwp hwp_act_window hwp_epp hwp_pkg_req avx512vbmi umip pku ospke waitpkg avx512_vbmi2 gfni vaes vpclmulqdq avx512_vnni avx512_bitalg tme avx512_vpopcntdq la57 rdpid bus_lock_detect cldemote movdiri movdir64b enqcmd fsrm md_clear serialize tsxldtrk pconfig arch_lbr amx_bf16 avx512_fp16 amx_tile amx_int8 flush_l1d arch_capabilities
我们把四台服务器的 IP 地址写到 nodefile 文件中,其中,第一行是主服务器。
cat << EOF > nodefile
192.168.20.2
192.168.21.2
192.168.22.2
192.168.23.2
EOF
分布式训练要求主节点和其他节点之间实现无密码 ssh 通信。如果你对此不是很熟悉,可以参考这篇 文章,并跟着它一步步设置好无密码 ssh 。
接下来,我们在每个节点上搭建运行环境并安装所需软件。我们特别安装了两个英特尔优化库: 用于管理分布式通信的 oneCCL 以及 Intel Extension for PyTorch (IPEX),IPEX 中包含了能充分利用 Sapphire Rapids 中的硬件加速功能的软件优化。我们还安装了 libtcmalloc ,它是一个高性能内存分配库,及其软件依赖项 gperftools 。
conda create -n diffuser python==3.9
conda activate diffuser
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
pip3 install transformers accelerate==0.19.0
pip3 install oneccl_bind_pt -f https://developer.intel.com/ipex-whl-stable-cpu
pip3 install intel_extension_for_pytorch
conda install gperftools -c conda-forge -y
下面,我们在每个节点上克隆 diffusers 代码库并进行源码安装。
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
cd diffusers
pip install .
紧接着,我们需要使用 IPEX 对 diffusers/examples/textual_inversion 中的微调脚本进行一些优化,以将 IPEX 对推理模型的优化包含在内 (译者注: diffusers 的设计中,其 pipeline 与 transformers 的 pipeline 虽然名称相似,但无继承关系,所以其子模型的推理优化无法在库内完成,只能在脚本代码内完成。而 Clip-Text 模型的微调由于使用了 accelerate ,所以其优化可由 accelerate 完成)。我们导入 IPEX 并对 U-Net 和变分自编码器 (VAE) 模型进行推理优化。最后,不要忘了这个改动对每个节点的代码都要做。
diff --git a/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion.py b/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion.py
index 4a193abc..91c2edd1 100644
--- a/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion.py
+++ b/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion.py
@@ -765,6 +765,10 @@ def main():
unet.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
vae.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
+ import intel_extension_for_pytorch as ipex
+ unet = ipex.optimize(unet, dtype=weight_dtype)
+ vae = ipex.optimize(vae, dtype=weight_dtype)
+
# We need to recalculate our total training steps as the size of the training dataloader may have changed.
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
if overrode_max_train_steps:
最后一步是下载 训练图像。一般我们会使用共享 NFS 文件夹,但为了简单起见,这里我们选择在每个节点上下载图像。请确保训练图像的目录在所有节点上的路径都相同 ( /home/devcloud/dicoo )。
mkdir /home/devcloud/dicoo
cd /home/devcloud/dicoo
wget https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library/dicoo/resolve/main/concept_images/0.jpeg
wget https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library/dicoo/resolve/main/concept_images/1.jpeg
wget https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library/dicoo/resolve/main/concept_images/2.jpeg
wget https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library/dicoo/resolve/main/concept_images/3.jpeg
wget https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library/dicoo/resolve/main/concept_images/4.jpeg
下面展示了我们使用的训练图像:
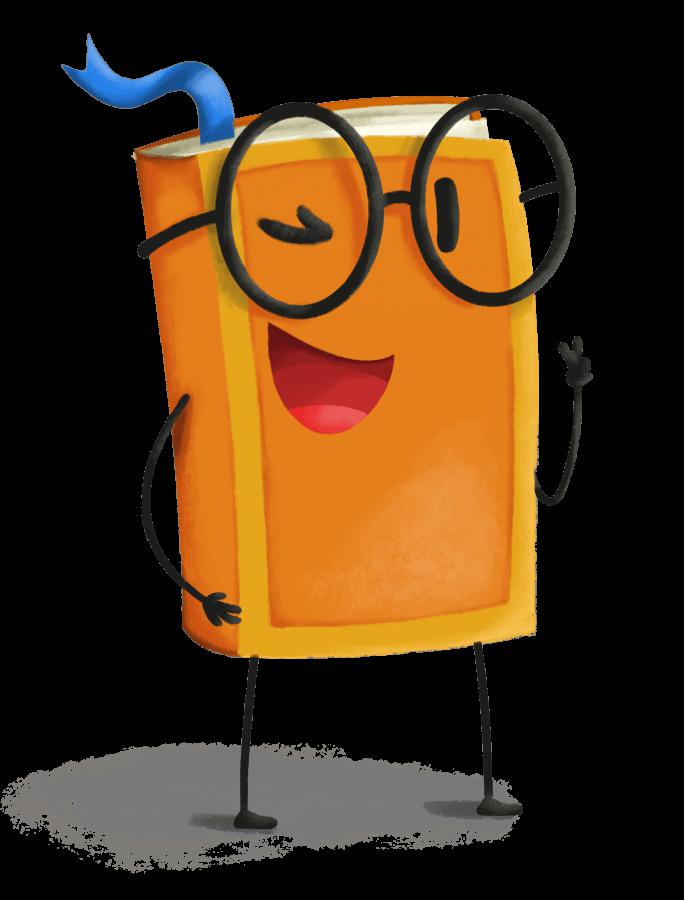
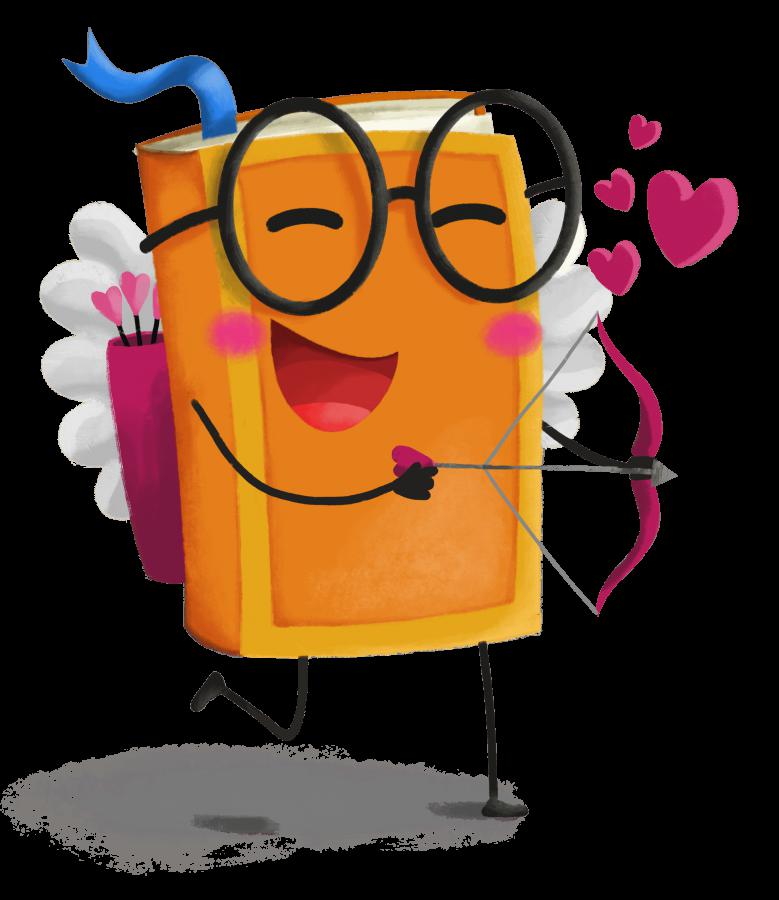
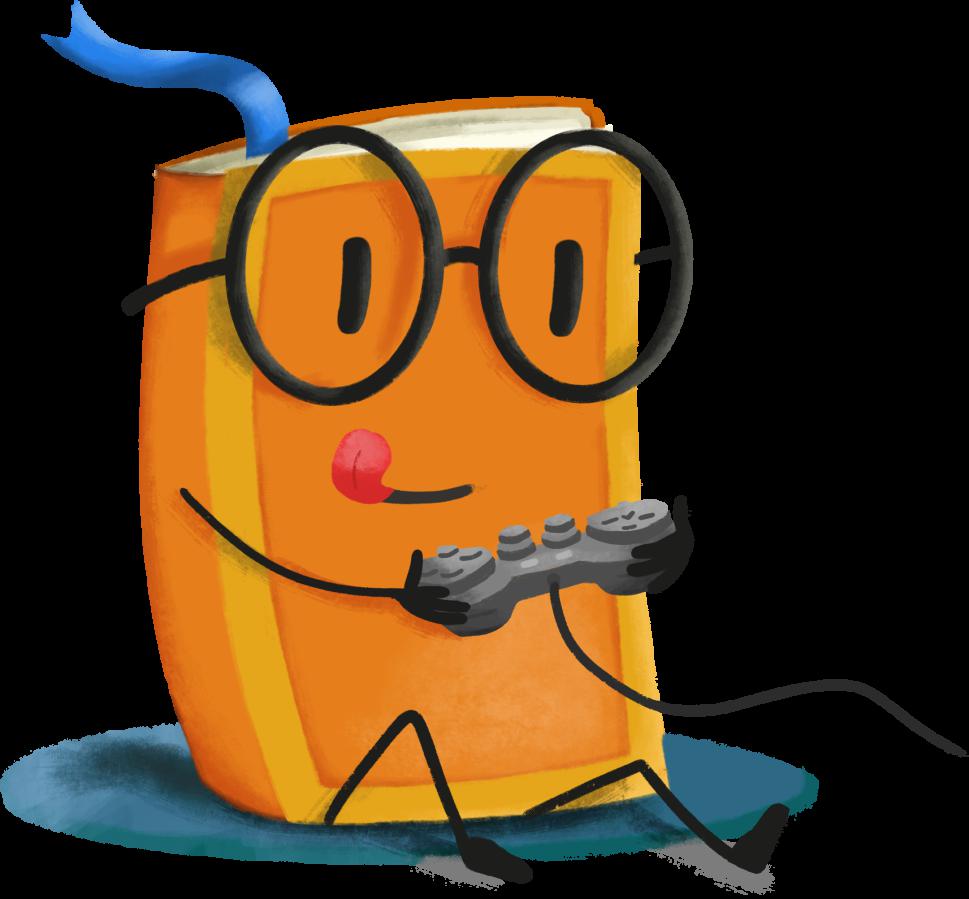
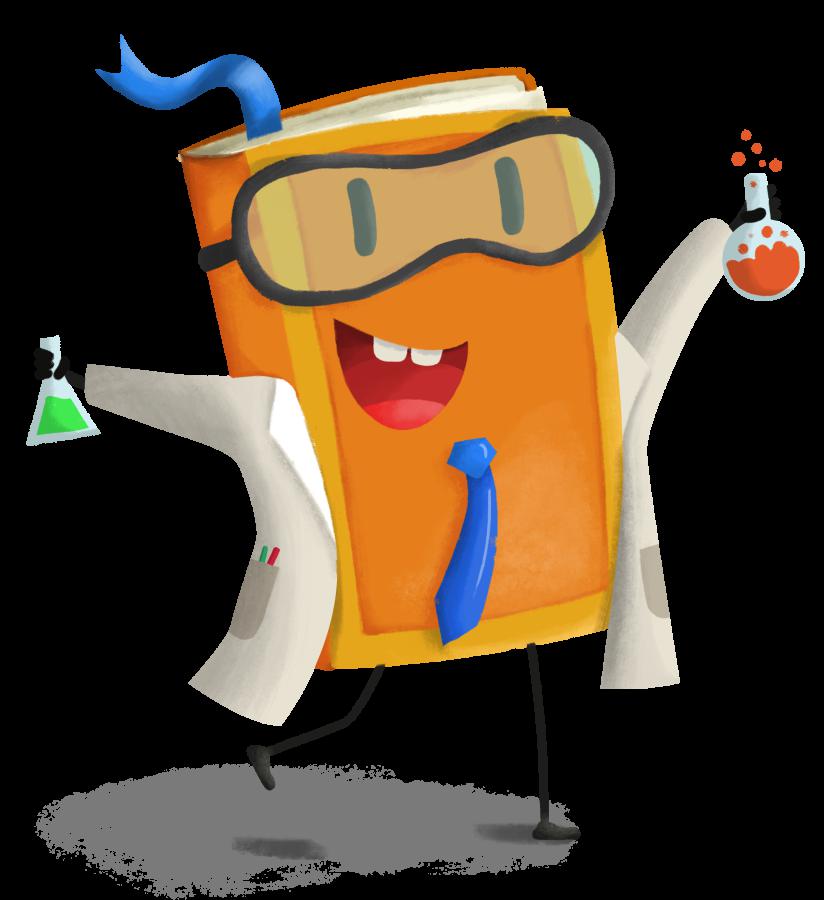





至此,系统配置就完成了。下面,我们开始配置训练任务。
配置微调环境
使用 accelerate 库让分布式训练更容易。我们需要在每个节点上运行 acclerate config 并回答一些简单问题。
下面是主节点的屏幕截图。在其他节点上,你需要将 rank 设置为 1、2 和 3,其他答案保持不变即可。
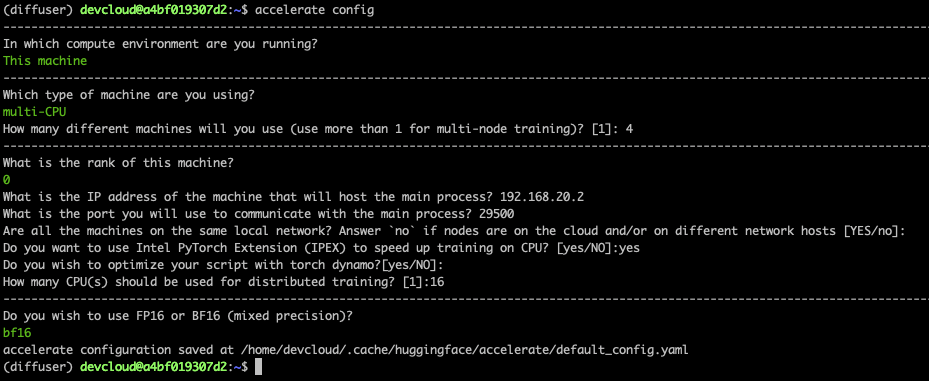
最后,我们需要在主节点上设置一些环境变量。微调任务启动时,这些环境变量会传播到其他节点。第一行设置连接到所有节点运行的本地网络的网络接口的名称。你可能需要使用 ifconfig 来设置适合你的网络接口名称。
export I_MPI_HYDRA_IFACE=ens786f1
oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch_path=$(python -c "from oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch import cwd; print(cwd)")
source $oneccl_bindings_for_pytorch_path/env/setvars.sh
export LD_PRELOAD=${LD_PRELOAD}:${CONDA_PREFIX}/lib/libiomp5.so
export LD_PRELOAD=${LD_PRELOAD}:${CONDA_PREFIX}/lib/libtcmalloc.so
export CCL_ATL_TRANSPORT=ofi
export CCL_WORKER_COUNT=1
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
export DATA_DIR="/home/devcloud/dicoo"
好了,现在我们可以启动微调了。
微调模型
我们使用 mpirun 启动微调,它会自动在 nodefile 中列出的节点之间建立分布式通信。这里,我们运行 16 个进程 ( -n ),其中每个节点运行 4 个进程 ( -ppn )。 Accelerate 库会自动在所有进程间建立分布式的训练。
我们启动下面的命令训练 200 步,仅需约 5 分钟。
mpirun -f nodefile -n 16 -ppn 4 \
accelerate launch diffusers/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion.py \
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME --train_data_dir=$DATA_DIR \
--learnable_property="object" --placeholder_token="<dicoo>" --initializer_token="toy" \
--resolution=512 --train_batch_size=1 --seed=7 --gradient_accumulation_steps=1 \
--max_train_steps=200 --learning_rate=2.0e-03 --scale_lr --lr_scheduler="constant" \
--lr_warmup_steps=0 --output_dir=./textual_inversion_output --mixed_precision bf16 \
--save_as_full_pipeline
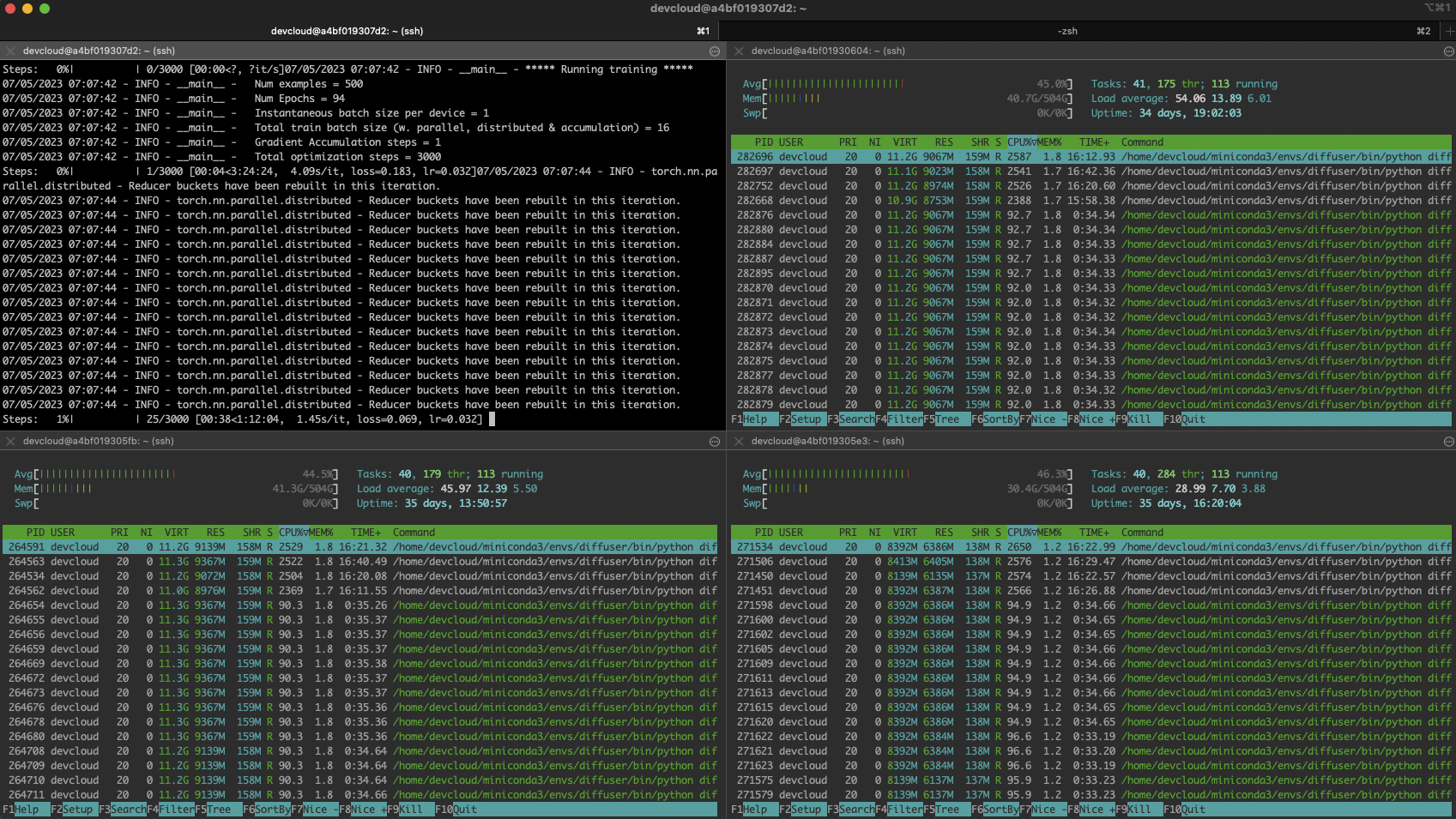
下面的截图显示了训练过程中集群的状态:
排障
分布式训练有时候会出现一些棘手的问题,尤其是当你新涉足于此。单节点上的小的配置错误是最可能出现的问题: 缺少依赖项、图像存储在不同位置等。
你可以登录各个节点并在本地进行训练来快速定位问题。首先,设置与主节点相同的环境,然后运行:
python diffusers/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion.py \
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME --train_data_dir=$DATA_DIR \
--learnable_property="object" --placeholder_token="<dicoo>" --initializer_token="toy" \
--resolution=512 --train_batch_size=1 --seed=7 --gradient_accumulation_steps=1 \
--max_train_steps=200 --learning_rate=2.0e-03 --scale_lr --lr_scheduler="constant" \
--lr_warmup_steps=0 --output_dir=./textual_inversion_output --mixed_precision bf16 \
--save_as_full_pipeline
如果训练成功启动,就停止它并移至下一个节点。如果在所有节点上训练都成功启动了,请返回主节点并仔细检查 nodefile 、环境以及 mpirun 命令是否有问题。不用担心,最终你会找到问题的 :)。
使用微调模型生成图像
经过 5 分钟的训练,训得的模型就保存在本地了,我们可以直接用 diffusers 的 pipeline 加载该模型并进行图像生成。但这里,我们要使用 Optimum Intel 和 OpenVINO 以进一步对模型进行推理优化。正如 上一篇文章 中所讨论的,优化后,仅用单颗 CPU 就能让你在不到 5 秒的时间内生成一幅图像!
pip install optimum[openvino]
我们用下面的代码来加载模型,并对其针对固定输出形状进行优化,最后保存优化后的模型:
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVStableDiffusionPipeline
model_id = "./textual_inversion_output"
ov_pipe = OVStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, export=True)
ov_pipe.reshape(batch_size=5, height=512, width=512, num_images_per_prompt=1)
ov_pipe.save_pretrained("./textual_inversion_output_ov")
然后,我们加载优化后的模型,生成 5 张不同的图像并保存下来:
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVStableDiffusionPipeline
model_id = "./textual_inversion_output_ov"
ov_pipe = OVStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, num_inference_steps=20)
prompt = ["a yellow <dicoo> robot at the beach, high quality"]*5
images = ov_pipe(prompt).images
print(images)
for idx,img in enumerate(images):
img.save(f"image{idx}.png")
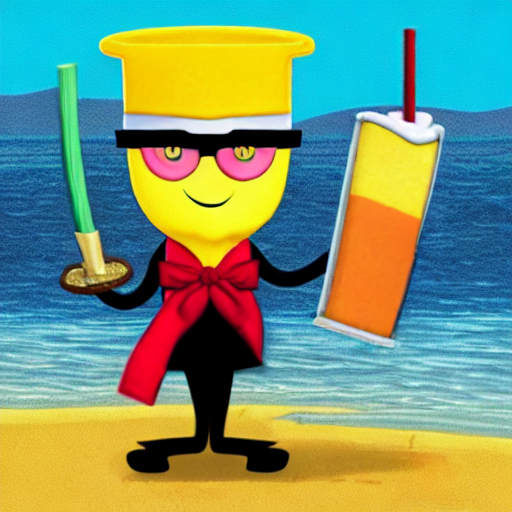
下面是其生成的图像。令人惊艳的是,模型只需要五张图像就知道 dicoo 是戴眼镜的!

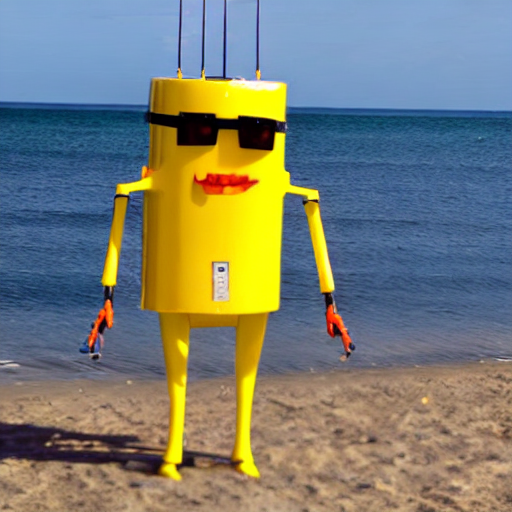
你还可以对模型进行更多的微调,以期获得更好的效果。下面是一个经 3 千步 (大约一个小时) 微调而得的模型生成的图像,效果相当不错。

总结
得益于 Hugging Face 和英特尔的深度合作,现在大家可以用至强 CPU 服务器来生成满足各自业务需求的高质量图像。而 CPU 通常比 GPU 等专用硬件更便宜且更易得,同时至强 CPU 还是个多面手,它可以轻松地用于其他生产任务,如 Web 服务器、数据库等等不一而足。因此,CPU 理所当然地成为了 IT 基础设施的一个功能全面且灵活的备选方案。
以下资源可供入门,你可按需使用:
- Diffusers 文档
- Optimum Intel 文档
- GitHub 上的 英特尔 IPEX
- 英特尔和 Hugging Face 的 开发者资源
- IDC、AWS 、GCP 以及 阿里云 上的第四代至强 CPU 实例
如果你有任何疑问或反馈,欢迎到 Hugging Face 论坛 留言。
感谢垂阅!

