Tiger Model
Enhancing Diagnostic Generalization of AI Models in Rare Thyroid Cancers: A Clinical Knowledge-Guided Data Augmentation Approach Using Generative Models
__Fang Dai†, Siqiong Yao†*, Min Wang, Yicheng Zhu, Xiangjun Qiu, Peng Sun, Jisheng Yin, Guangtai Shen, Jingjing Sun, Maofeng Wang, Yun Wang, Zheyu Yang, Jianfeng Sang, Xiaolei Wang, Fenyong Sun*, Wei Cai*, Xingcai Zhang*, Hui Lu*__
* To whom correspondence should be addressed.
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Email: huilu@sjtu.edu.cn.
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology imaging struggles with diagnosing rare tumors. Our study identified performance gaps in detecting rare thyroid cancer subtypes using ultrasound, leading to misdiagnoses and adverse prognostic outcomes. Sample scarcity for rare conditions impedes effective model training. Although data augmentation techniques can alleviate sample size constraints, trainable examples cannot encompass the full spectrum of disease manifestations, rendering traditional generative augmentation approaches inadequate. Our approach integrates clinical knowledge with text-image generation, enabling fine-grained control and supplementation of unique features specific to rare subtypes, emphasizing text guidance. This results in augmented samples that more accurately reflect genuine disease cases. Our model, trained on data from 40,571 patients, including 5,099 rare cases, exceeds current state-of-the-art methods, enhancing the AUC for two rare subtypes by 14.64% and 9.45%, respectively. In Turing tests, we achieved 92.2% for authenticity, 90.96% for consistency, and 84.1% for diversity, surpassing competitors by 35.6%. Generalization ability of this methodology was validated on public datasets such as the BrEaST, BUSI, and VinDr-PCXR datasets. This approach mitigates the challenges of data diversity and representativeness for rare diseases, contributing to the model’s generalization ability and diagnostic accuracy, ultimately improving the effectiveness and practical outcomes of medical AI applications.
 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: This image is protected by copyright laws and is the property of [Fang Dai/Shanghai Jiao Tong University]. Unauthorized copying, distribution, or use of this image is strictly prohibited. All rights reserved.
COPYRIGHT NOTICE: This image is protected by copyright laws and is the property of [Fang Dai/Shanghai Jiao Tong University]. Unauthorized copying, distribution, or use of this image is strictly prohibited. All rights reserved.
Research Status: Under Review
Model architecture
The model architecture is included in the manuscript and will not be displayed before the article is published.
Install
This project uses requirements.txt.
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
Datasets
- Thyroid dataset for Tiger Model (The other external validation datasets(BrEaST, BUSI, VinDr-PCXR) are also deployed in folders in the same manner.)
├─dataset
└─training data
├─init_image
20191101_094744_1.png
... ...
metadata.jsonl
├─condition_FG
20191101_094744_1.png
... ...
├─condition_BG
20191101_094744_1.png
... ...
- Thyroid dataset for Resnet Model (The other external validation datasets(BrEaST, BUSI, VinDr-PCXR) are also deployed in folders in the same manner.)
├─dataset
│ ├─Renset training data
│ │ └─PTC
│ │ └─train
│ │ └─0
│ │ figure1.jpg
... ...
│ │ └─1
│ │ figure2.jpg
... ...
│ │ └─valid
│ │ └─0
│ │ figure3.jpg
... ...
│ │ └─1
│ │ figure4.jpg
... ...
│ │ └─test
│ │ └─0
│ │ figure5.jpg
... ...
│ │ └─1
│ │ figure6.jpg
... ...
│ │ └─FTC
... ...
│ │ └─MTC
... ...
Partial thyroid ultrasonography data used in this study are subject to privacy restrictions, but may be anonymized and made available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Training data preparation
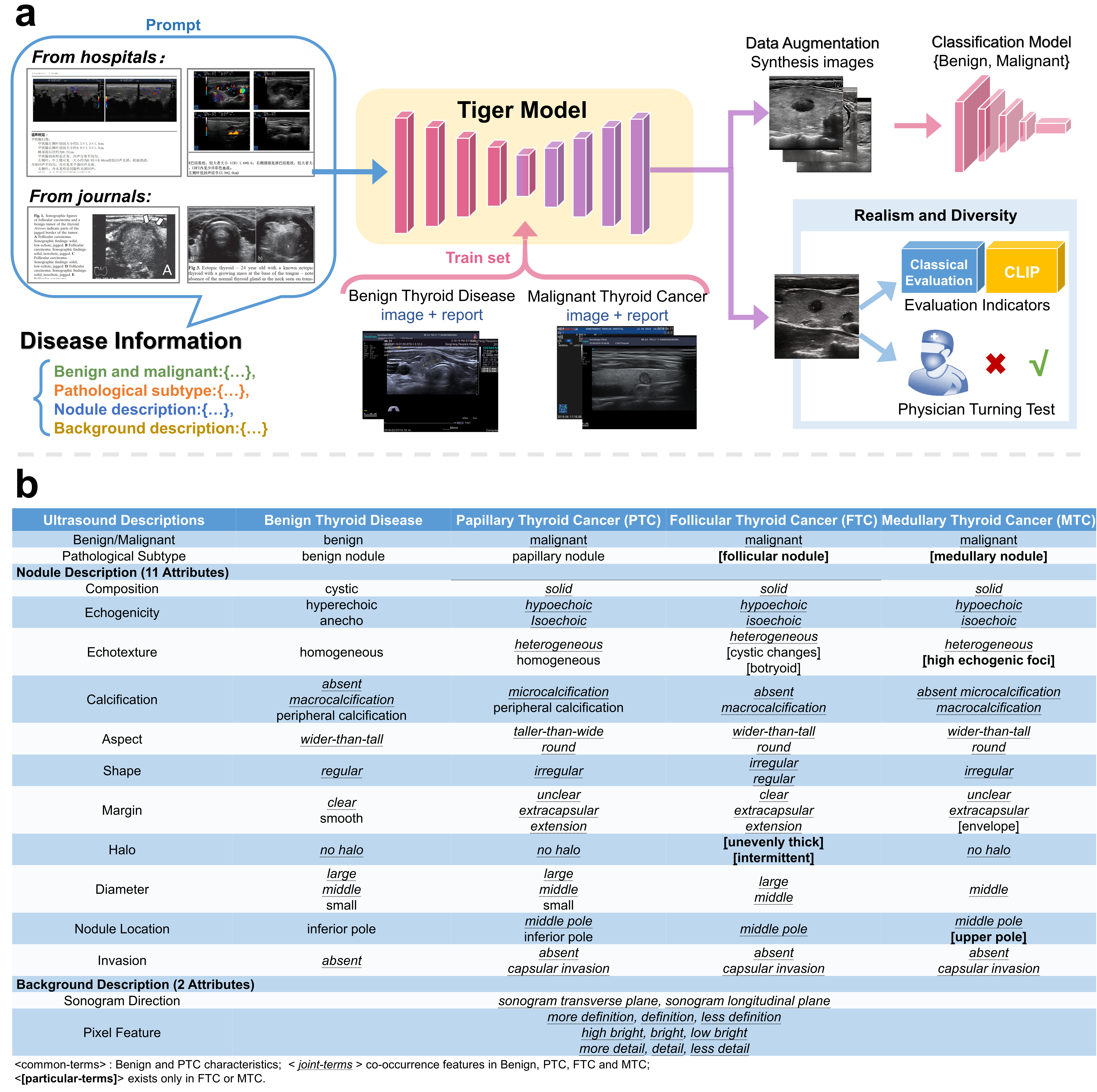
metadata.josnl: The file is placed under folder dataset/training data/init_image, each of which acts as the file name of the image, the associated condition file, and text information to facilitate the subsequent import of the model
| {"file_name": "20191101_094744_1.png", "condition_FG": "../training data/condition_nd/20191101_094744_1.png", "condition_BG": "../training data/condition_bg/20191101_094744_1.png", "text_nd": "papillary, wider-than-tall, clear, regular", "text_bg": "145.819221, 51.008308, 2.096069"}\
| {... ...}
Installation
We recommend installing Tiger Model in a virtual environment via Conda. For more detailed information about installing PyTorch, please refer to the official documentation.
PyTorch-diffusers (including Stable Diffusion, ControlNet, Transformer)
With pip (official package):
pip install --upgrade diffusers[torch]
With conda (maintained by the community):
conda install -c conda-forge diffusers
PyTorch-Others
conda list -e > requirements.txt
Tiger Model Coarse-Training
Coarse-Training: based on the Stable Diffusion (SD) model . Training utilizes ultrasound images and corresponding textual reports (Image + Prompt) as inputs. During this phase, the model is able to generate coarse-grained image features based on text.
$ sh ./Tiger-Corase.sh
Tiger Model Fine-Training
To optimize details, utilized the trainable Encoder weights from the Coarse-Training model , and employed the conditional control method similar to ControlNet but with some differences.
$ sh ./Tiger-Fine.sh
Trained Model Release: Tiger
This repository contains the trained model for Tiger designed for thyroid image generation. The model was trained on stable diffusion using PyTorch.
Model Details
- Model Architecture: [stable-diffusion-v2]
- Input Size: [224x224 for images]
- Output: [image]
- Framework: [PyTorch]
- Download Link 1: google drive link to download the Coarse-Training model]
- Download Link 2: google drive link to download the Fine-Training model]
Tiger Model Inference
Tiger Model's application scenarios (inference) can be divided into two categories (Supplementary Fig.3). The first type is Diversify Inference, which involves generating thyroid feature textual prompts based on prompt input combinations. Tiger Model generates synthetic images based on the prompt content, controlling the synthesis of corresponding fine-grained foreground-background features within the model. The second type is Reference Inference, where the input comprises real images. Tiger Model generates images consistent with the subtype of the input image. Both generation scenarios allow for the control of corresponding foreground-background features as needed during the generation process.
$ python Tiger Model/generation.py
Binary classification Resnet50 training
In the training stage, the generated image and the real image are mixed together to train the classification model.
$ sh ResnNet_main.sh
Evaluation criteria
CLIP score
The CLIP scoring criteria involve training a CLIP model and calculating the CLIP score based on the corresponding CLIP values from the model. For specific calculation methods, please refer to the appendix. The CLIP training code is referenced from this study.
Moso score
We employ the MoSo score to control the quality of generated images, which measures the change in the optimal empirical risk after the exclude of a particular sample from the training set.
Reference
All references are listed in the article.
Licence
The code is distributed under the Apache License 2.0. It can be used for non-commercial purposes only after the publication of the article. For any commercial use, please contact the author for permission.
- Downloads last month
- 0
