license: gpl-3.0
language:
- en
- zh
Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1
- Main Page:Fengshenbang
- Github: Fengshenbang-LM
姜子牙系列模型
简介 Brief Introduction
姜子牙通用大模型V1是基于LLaMa的130亿参数的大规模预训练模型,具备翻译,编程,文本分类,信息抽取,摘要,文案生成,常识问答和数学计算等能力。目前姜子牙通用大模型已完成大规模预训练、多任务有监督微调和人类反馈学习三阶段的训练过程。
The Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1 is a large-scale pre-trained model based on LLaMA with 13 billion parameters. It has the ability to perform tasks such as translation, programming, text classification, information extraction, summarization, copywriting, common sense Q&A, and mathematical calculation. The Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1 has undergone three stages of training: large-scale continual pre-training (PT), multi-task supervised fine-tuning (SFT), and human feedback learning (RM, PPO).
模型分类 Model Taxonomy
| 需求 Demand | 任务 Task | 系列 Series | 模型 Model | 参数 Parameter | 额外 Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 通用 General | AGI模型 | 姜子牙 Ziya | LLaMA | 13B | English&Chinese |
模型信息 Model Information
继续预训练 Continual pretraining
原始数据包含英文和中文,其中英文数据来自openwebtext、Books、Wikipedia和Code,中文数据来自清洗后的悟道数据集、自建的中文数据集。在对原始数据进行去重、模型打分、数据分桶、规则过滤、敏感主题过滤和数据评估后,最终得到125B tokens的有效数据。
为了解决LLaMA原生分词对中文编解码效率低下的问题,我们在LLaMA词表的基础上增加了7k+个常见中文字,通过和LLaMA原生的词表去重,最终得到一个39410大小的词表,并通过复用Transformers里LlamaTokenizer来实现了这一效果。
在增量训练过程中,我们使用了160张40GB的A100,采用2.6M tokens的训练集样本数量和FP 16的混合精度,吞吐量达到118 TFLOP per GPU per second。因此我们能够在8天的时间里在原生的LLaMA-13B模型基础上,增量训练110B tokens的数据。
训练期间,虽然遇到了机器宕机、底层框架bug、loss spike等各种问题,但我们通过快速调整,保证了增量训练的稳定性。我们也放出训练过程的loss曲线,让大家了解可能出现的问题。
The original data contains both English and Chinese, with English data from openwebtext, Books, Wikipedia, and Code, and Chinese data from the cleaned Wudao dataset and self-built Chinese dataset. After deduplication, model scoring, data bucketing, rule filtering, sensitive topic filtering, and data evaluation, we finally obtained 125 billion tokens of valid data.
To address the issue of low efficiency in Chinese encoding and decoding caused by the native word segmentation of LLaMa, we added 8,000 commonly used Chinese characters to the LLaMa vocabulary. By removing duplicates with the original LLaMa vocabulary, we finally obtained a vocabulary of size 39,410. We achieved this by reusing the LlamaTokenizer in Transformers.
During the incremental training process, we used 160 A100s with a total of 40GB memory, using a training dataset with 2.6 million tokens and mixed precision of FP16. The throughput reached 118 TFLOP per GPU per second. As a result, we were able to incrementally train 110 billion tokens of data on top of the native LLaMa-13B model in just 8 days.
Throughout the training process, we encountered various issues such as machine crashes, underlying framework bugs, and loss spikes. However, we ensured the stability of the incremental training by making rapid adjustments. We have also released the loss curve during the training process to help everyone understand the potential issues that may arise.

多任务有监督微调 Supervised finetuning
在多任务有监督微调阶段,采用了课程学习(curiculum learning)和增量训练(continual learning)的策略,用大模型辅助划分已有的数据难度,然后通过“Easy To Hard”的方式,分多个阶段进行SFT训练。
SFT训练数据包含多个高质量的数据集,均经过人工筛选和校验:
- Self-Instruct构造的数据(约2M):BELLE、Alpaca、Alpaca-GPT4等多个数据集
- 内部收集Code数据(300K):包含leetcode、多种Code任务形式
- 内部收集推理/逻辑相关数据(500K):推理、申论、数学应用题、数值计算等
- 中英平行语料(2M):中英互译语料、COT类型翻译语料、古文翻译语料等
- 多轮对话语料(500K):Self-Instruct生成、任务型多轮对话、Role-Playing型多轮对话等
During the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) phase of multitask learning, we used a strategy of curriculum learning and incremental training. We used the large model to assist in partitioning the existing data by difficulty and then conducted SFT training in multiple stages using the "easy to hard" approach.
The SFT training data consists of multiple high-quality datasets that have been manually selected and verified, including approximately 2 million samples from datasets such as BELLE, Alpaca, and Alpaca-GPT4, 300,000 samples of internally collected code data including LeetCode and various code tasks, 500,000 samples of internally collected inference/logic-related data such as reasoning, argumentative essays, mathematical application questions, and numerical calculations, 2 million samples of Chinese-English parallel corpora including translation, COT-type translation, and classical Chinese translation, and 500,000 samples of multi-turn dialogue corpora including self-instructed generation, task-oriented multi-turn dialogue, and role-playing multi-turn dialogue.
人类反馈学习 Human-Feedback training
为了进一步提升模型的综合表现,使其能够充分理解人类意图、减少“幻觉”和不安全的输出,基于指令微调后的模型,进行了人类反馈训练(Human-Feedback Training,HFT)。在训练中,我们采用了以人类反馈强化学习(RM、PPO)为主,结合多种其他手段联合训练的方法,手段包括人类反馈微调(Human-Feedback Fine-tuning,HFFT)、后见链微调(Chain-of-Hindsight Fine-tuning,COHFT)、AI反馈(AI Feedback)和基于规则的奖励系统(Rule-based Reward System,RBRS)等,用来弥补PPO方法的短板,加速训练。
我们在内部自研的框架上实现了HFT的训练流程,该框架可以利用最少8张40G的A100显卡完成Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1的全参数训练。在PPO训练中,我们没有限制生成样本的长度,以确保长文本任务的奖励准确性。每次训练的总经验池尺寸超过100k样本,确保了训练的充分性。
To further improve the overall performance of the model, enabling it to fully understand human intentions, reduce "hallucinations" and unsafe outputs, we conducted Human-Feedback Training (HFT) based on the model fine-tuned with instructions. In the training process, we used a variety of methods, including human feedback reinforcement learning (RM, PPO), combined with other methods such as Human-Feedback Fine-tuning (HFFT), Chain-of-Hindsight Fine-tuning (COHFT), AI feedback, and Rule-based Reward System (RBRS), to supplement the shortcomings of the PPO method and accelerate training.
We implemented the HFT training process on an internally developed framework, which can use a minimum of 8 40GB A100 GPUs to complete the full parameter training of Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1. In the PPO training, we did not limit the length of the generated samples to ensure the accuracy of rewards for long-text tasks. The total experience pool size for each training exceeded 100k samples, ensuring the sufficiency of the training.
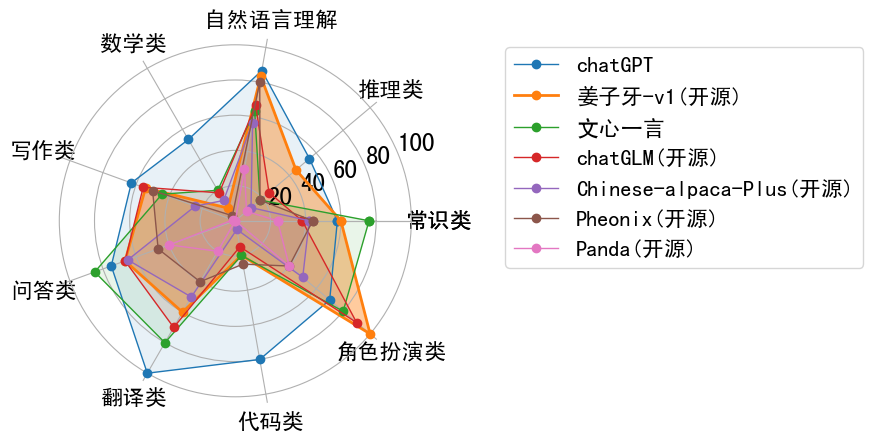
效果评估 Performance
使用 Usage
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from transformers import LlamaForCausalLM
import torch
device = torch.device("cuda")
query="帮我写一份去西安的旅游计划"
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained('IDEA-CCNL/Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1', torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('IDEA-CCNL/Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1')
inputs = '<human>:' + query.strip() + '\n<bot>:'
input_ids = tokenizer(inputs, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(device)
generate_ids = model.generate(
input_ids,
max_new_tokens=1024,
do_sample = True,
top_p = 0.85,
temperature = 1.0,
repetition_penalty=1.,
eos_token_id=2,
bos_token_id=1,
pad_token_id=0)
output = tokenizer.batch_decode(generate_ids)[0]
print(output)
引用 Citation
如果您在您的工作中使用了我们的模型,可以引用我们的论文:
If you are using the resource for your work, please cite the our paper:
@article{fengshenbang,
author = {Jiaxing Zhang and Ruyi Gan and Junjie Wang and Yuxiang Zhang and Lin Zhang and Ping Yang and Xinyu Gao and Ziwei Wu and Xiaoqun Dong and Junqing He and Jianheng Zhuo and Qi Yang and Yongfeng Huang and Xiayu Li and Yanghan Wu and Junyu Lu and Xinyu Zhu and Weifeng Chen and Ting Han and Kunhao Pan and Rui Wang and Hao Wang and Xiaojun Wu and Zhongshen Zeng and Chongpei Chen},
title = {Fengshenbang 1.0: Being the Foundation of Chinese Cognitive Intelligence},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2209.02970},
year = {2022}
}
You can also cite our website:
欢迎引用我们的网站:
@misc{Fengshenbang-LM,
title={Fengshenbang-LM},
author={IDEA-CCNL},
year={2021},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/IDEA-CCNL/Fengshenbang-LM}},
}